At the start of every semester for as long as I can remember, I have invited people to sit in informally on my classes at NYU or take the shorter online versions on my website. After thirty six years of teaching, you would think I would be jaded, but I am not. As we get ready for the spring, I am excited, perhaps more so than usual, because I hope to finally be in a real classroom, instead of online, for my classes.
Spring is here, and the classroom beckons!
I have always described myself as a teacher, first and foremost, but like many of you, COVID has been a disruptor. For much of the last two years, rather than teach my classes in a classroom, I taught my classes from my home office, making a few low-cost, low-tech investments to improve my set up.
I know that many of us, especially as we age, take the dystopian view that technology has hurt more than helped, and while I share the concern about the damage that social media has wrought on society, I remain thankful for the good that has come from technological advances. The combination of speedy internet access and delivery platforms (Zoom, Teams, Skype, Blue Jeans etc.) allowed me to deliver my classes from home, with some help. With a M1 MacBook Pro, a 27 inch LG display and my iPad Pro in sidecar mode, I could see everyone in my class, albeit with some work; with Zoom, the limit was 48 students at a time. My Rode Go lav mike and my AirPods Pro, took care of my audio needs, and my Logitech C920 camera supplemented my computer's camera to cover my video requirements, with two extra spotlights for late evening sessions, when natural light failed. To top it all off, and this was priceless, I could see the Pacific Ocean, out of my window, especially when I was able to teach standing, using my Flexispot standing desk to elevate my monitor. (If you are wondering why I have been so specific about my accessories, it is not because I receive sponsorship payments from any of these companies, but because it may help you replicate my set up, other than the view of the Pacific, if you are teaching or working from home. If you have a bigger budget, I would try to emulate Professor Andrew Lo, who described his astounding set up for teaching last year.)
In these last two years, I have learned a lot about online teaching and I hope that learning makes me a better teacher, both online and in the classroom.
- First, with today's technology, online classes get scarily close to physically being in a classroom, a reminder to me, and teachers all over the world, that unless we offer something unique in a classroom setting, disruption is coming for the teaching business.
- Second, I learned there is some learning that is better delivered online, than in a physical setting, and I believe that there are some topics that I will continue to deliver online, even after this virus passes on.
- Third, while I still loved teaching online, I desperately missed the feeling of being in an actual classroom, looking at a collection of faces, some with eyes closed, some bored and some waiting to ask a question. After all, every teacher is a repressed actor, and actors draw their energy from their audiences, and I have been missing mine!
Classes
I am a dabbler, not a specialist, and my teaching reflects that predisposition. During my teaching lifetime, I have taught a wide swath of classes, ranging from banking to equity instruments, but in the last twenty years, my focus has been on three classes, corporate finance, valuation and investment philosophies, with the last one taught only online. My classroom teaching at Stern has been mostly corporate finance and valuation, to both MBAs and undergraduates. With MBAs, the corporate finance class has been a first year elective and the valuation has been an elective in the second year, and with undergraduates, I have alternated between the two classes across the years. I have added shorter online versions of each class, offered on my website, at no cost, but with no credit. Starting a few years ago, Stern has offered certificate versions of each of the three classes, albeit at a price, but with more structure (quizzes, exams, projects) and a certificate, if you make it through.
Pre-Game Prep
In all of my regular classes, I have drawn on the assumption that my students come in with an exposure and understanding of three areas, accounting (more in the context of being able to read financial statements than the mechanics of debit and credit), basics of finance (especially the time value of money and an understanding of markets) and statistics (how to make sense of data). Being a control freak, I have created my own versions of what I would like my students to know in each of these disciplines, and you can find my versions on my website. With each of my classes, I am sure that purists in each of these areas would blanch not just at my choice of topics that matter, but also at my sloppiness in description, but I will let you be the judge of content.
The place to start is with accounting. Much as I abuse accountants in my classroom, I also recognize that almost all of the raw material we use in corporate finance and valuation comes from accounting statements. Put simply, if you cannot tell the difference between operating and net income, or what to consider as debt, you will be lost in any type of financial analysis. In my eleven-session (with each session lasting 15-20 minutes) accounting class, I cover the material that I draw on in my finance classes:
 |
| Web page for class |
Once you have the accounting basics under your belt, you can turn to the basics of finance. The time value of money is at the heart of almost everything in finance, and understanding the mechanics and intuition of present value is a bedrock on financial analysis. In my introductory finance class, I cover the time value of money, and how risk plays out in that computation, as well as look at three macro variables that we encounter repeatedly in financial analyses - inflation, interest rates and exchange rates.
 |
| Web page for class |
 |
| Web page for class |
The Game
If you have the pre-game behind you, it is time to turn to the main attractions (or tortures, depending on your perspective), and I will present them in the sequence that I think it makes the most sense to take them, if you want to torture yourself by taking all three.
a. Corporate Finance
If you have taken a corporate finance class in your past life, you may be surprised by what I cover, and what I do not, in my corporate finance class. My version of the class should have a different name, since it is not just about corporations and I am not sure that it is all about finance either. It covers the first financial principles that govern how to run a business, and as a consequence, it has the broadest reach and the deepest impact of any of my classes. Whether you are an entrepreneur, starting on the long process of converting an idea into a business, a manager, evaluating how to make business decisions consistently or a consultant, offering advice on what a business should do differently, corporate finance is your go-to class, since it offers guiding principles for all your tasks. I start the class with a one-page summary of the entire class:
 |
| Web page for class |
I will be teaching this class to Stern MBAs, starting on January 31, 2022, meeting every Monday and Wednesday, from 10.30 am - 11.50 am, New York time, through May 9, 2022. If you are a Stern MBA, you are welcome to take the class, but if you are not, you can take the class informally, by watching the recorded sessions at this link, taking the quizzes and exam, if you are up for them, and even tracking the emails that I send the class at this link. Since the 26 sessions of the class are 80 minutes apiece, this will require a substantial investment in time, though no investment in money, albeit with no certification or credit. If that time investment is too much of a burden, I have created an online version of the class here, with 15-minute sessions replacing the longer classroom sessions, and while they will cost you nothing as well, they come with no certification. If certification is your end game, and I understand that it may help augment a resume, you can take the NYU version of the online class in the fall of 2022, with a more polished interface and personal interaction, but the same content, where you will get a certification and NYU will get a portion of your savings.
b. Valuation
My valuation class starts with an ambitious agenda, i.e., to give you the tools and techniques to value or price just about anything, from bitcoin to collectibles to infrastructure projects, and from any perspective, from a potential buyer to an accountant estimating fair value.
 |
| Web page for class |
This class will be taught to two different audiences, Stern MBAs, many of whom were in my corporate finance class last spring, and Stern undergraduates, mostly juniors. While the first group will meet every Monday and Wednesday, from 1.30 pm - 2.50 pm, from January 31, 2022, to May 9, 2022, and the second will meet every Monday and Wednesday from 3.30 pm - 4.45 pm, from January 24, 2022, to May 9, 2022, the classes are identical in content and delivery. You are welcome to unofficially partake in either of these classes, both in recorded form, but as with corporate finance, you can take an online version of the valuation class, with twenty six shorter (15-minute) sessions, for free, with no certification, on my site, or for a price and a certificate from NYU.
c. Investment Philosophy
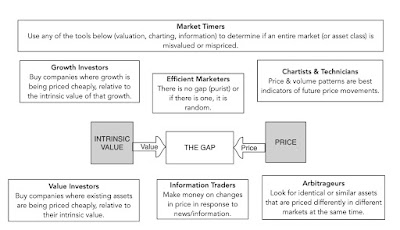
This class has its origins in a seminar class that I was asked to teach more than twenty years ago, where successful investors would come in each session and talk about what they did in investing that made them successful. As we transitioned from technical analysts to value and growth investors to market timers, each of whom was successful, albeit with wildly different views of markets and divergent paths to success, I concluded that there could not be one template for investment success, and started looking at not only differences in investment philosophies, but also what personal qualities made for success, with each one. That led to a book, and then to a class on investment philosophies, where I cover the range of choices.
 |
| Web page for class |
If there are two lessons that I hope that people take away from this class, it is (a) that no investment philosophy, no matter how storied and successful it has been in the past, has a monopoly on investment virtue and that (b) the right investment philosophy for you is the one that best fits your personality and strengths.
While I do not teach this course in a classroom, there are two ways you can take the class. One is online, on my website, where I lead you through a journey through different investment philosophies, weighing not just past successes, but also the combination of factors that you need to have to succeed each one, over the course of 36 sessions. As with the other online classes on my site, it is free, but without certification. If you do want certification, there is the NYU version of the class available here, but for a price (that I do not set or control... so it is not fair to argue its fairness or unfairness with me).
Game Plan
While I hope that the descriptions of the classes will help you decide which of these courses best fits you, you may still be confused about the choices and the sequence. I hope that the flow chart below provides a little more clarity:
 |
| Web page for all classes |
YouTube Video
Class List
- Accounting for finance and investing (My webpage, YouTube Playlist)
- Foundations of Finance (My webpage, YouTube Playlist)
- Statistics for finance and investing (My webpage, YouTube Playlist)
- Corporate Finance (Spring 2022 MBA Class, Free Online, NYU Certificate in Fall 2022)
- Valuation (Spring 2022 MBA Class, Spring 2022 Undergraduate Class, Free Online, NYU Certificate)
- Investment Philosophies (Free Online, NYU Certificate)